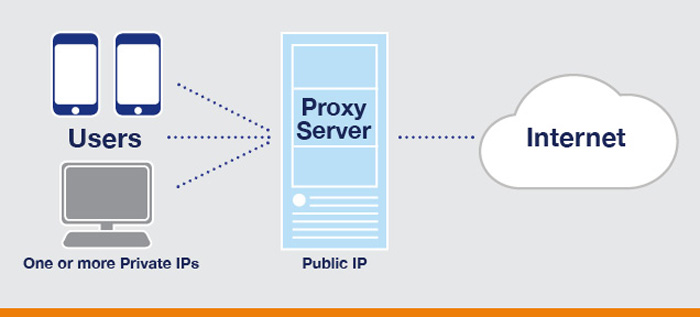
A proxy server, also known as a proxy or application-level gateway, is a computer that acts as a gateway between a local network (e.g., all the computers at one company or in one building) and a larger-scale network such as the Internet.
Proxy servers provide increased performance and security.
In some cases, they monitor employees' use of outside resources.
A proxy server works by intercepting connections between sender and receiver.
All incoming data enters through one port and is forwarded to the rest of the network via another port. By blocking direct access between two networks, proxy servers make it much more difficult for hackers to get internal addresses and details of a private network.
Some proxy servers are a group of applications or servers that block common Internet services.
For example, an HTTP proxy intercepts web access, and an SMTP proxy intercepts email.
A proxy server uses a network addressing scheme to present one organization-wide IP address to the Internet.
The server funnels all user requests to the Internet and returns responses to the appropriate users. In addition to restricting access from outside, this mechanism can prevent inside users from reaching specific Internet resources (e.g., certain websites).
A proxy server can also be one of the components of a firewall.
_________________________
_________________________
Comments
Post a Comment